6 Immediate Drug Allergy
For an overview of immediate drug allergy testing, I recommend getting started by watching Immediate Drug Allergy Hypersensitivity Testing.
Skin Testing
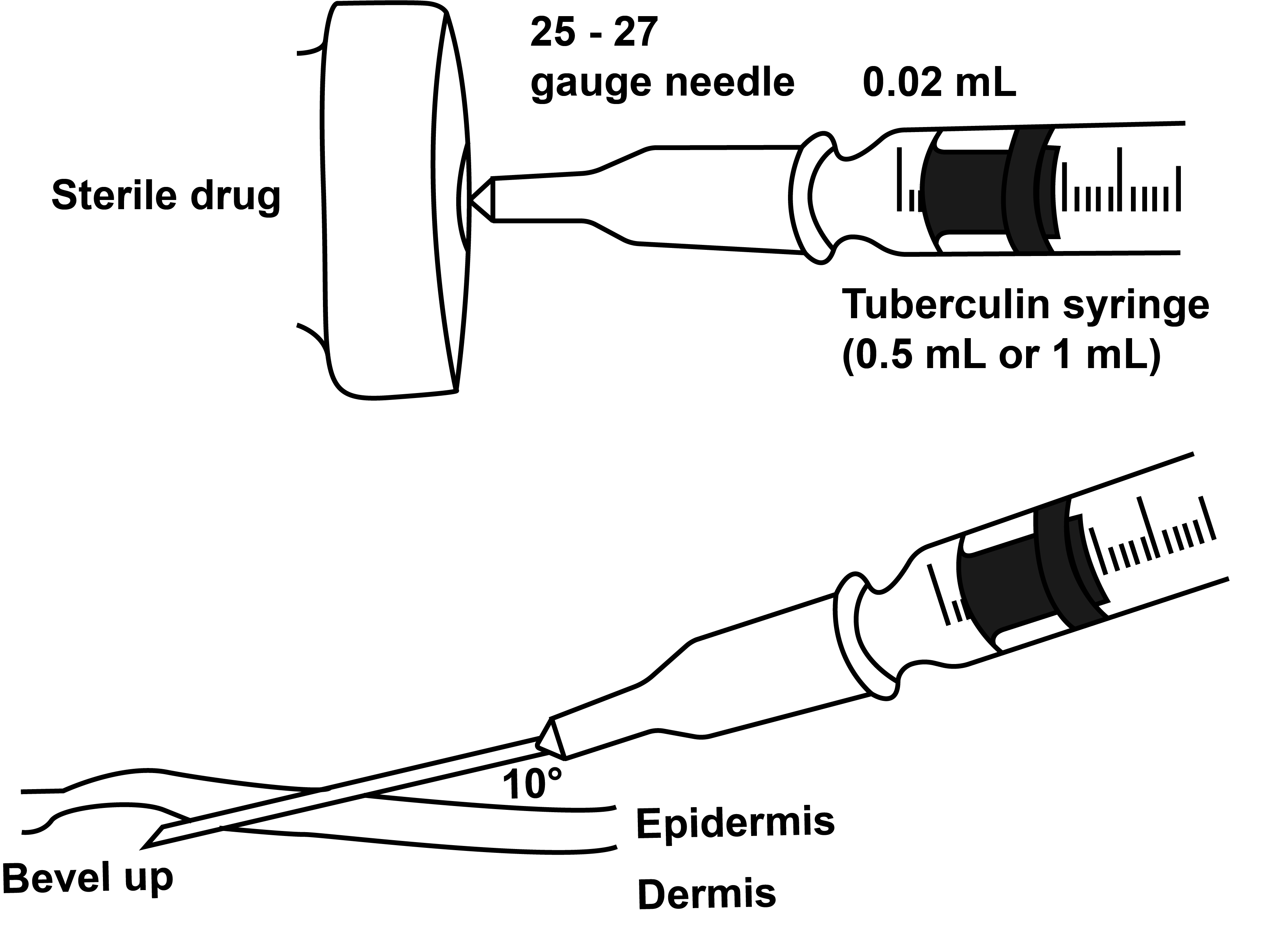
Concentrations typically employed for drug skin testing are 1:10, 1:100, and full strength.
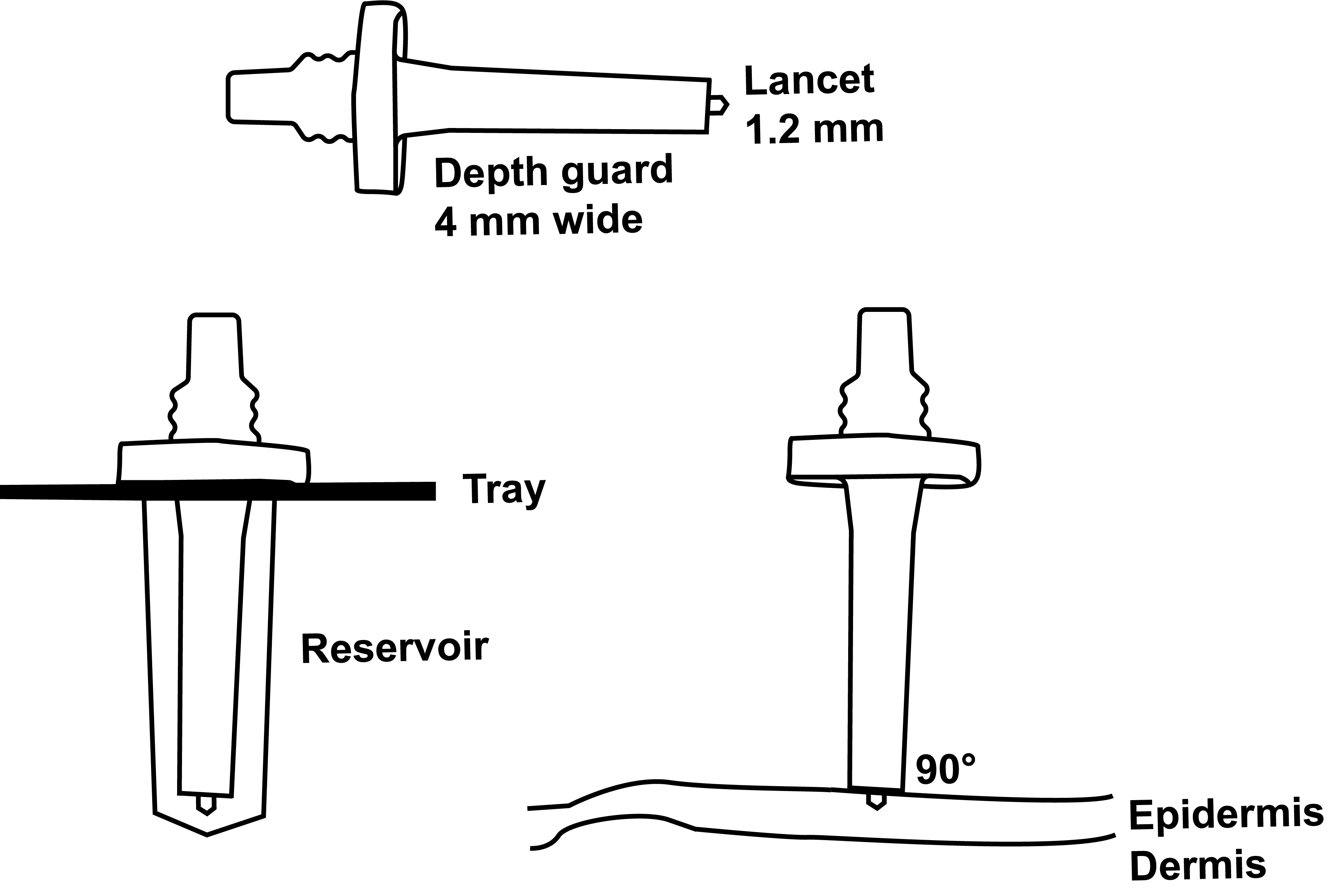
Should be performed on healthy, non-pathologic skin. For example skin with altered permeability (e.g. atopic dermatitis), the amount of allergen penetrating the skin is up to 20x greaterh than the average volume of inoculum by SPT.
Skin Prick Testing
Intradermal Testing
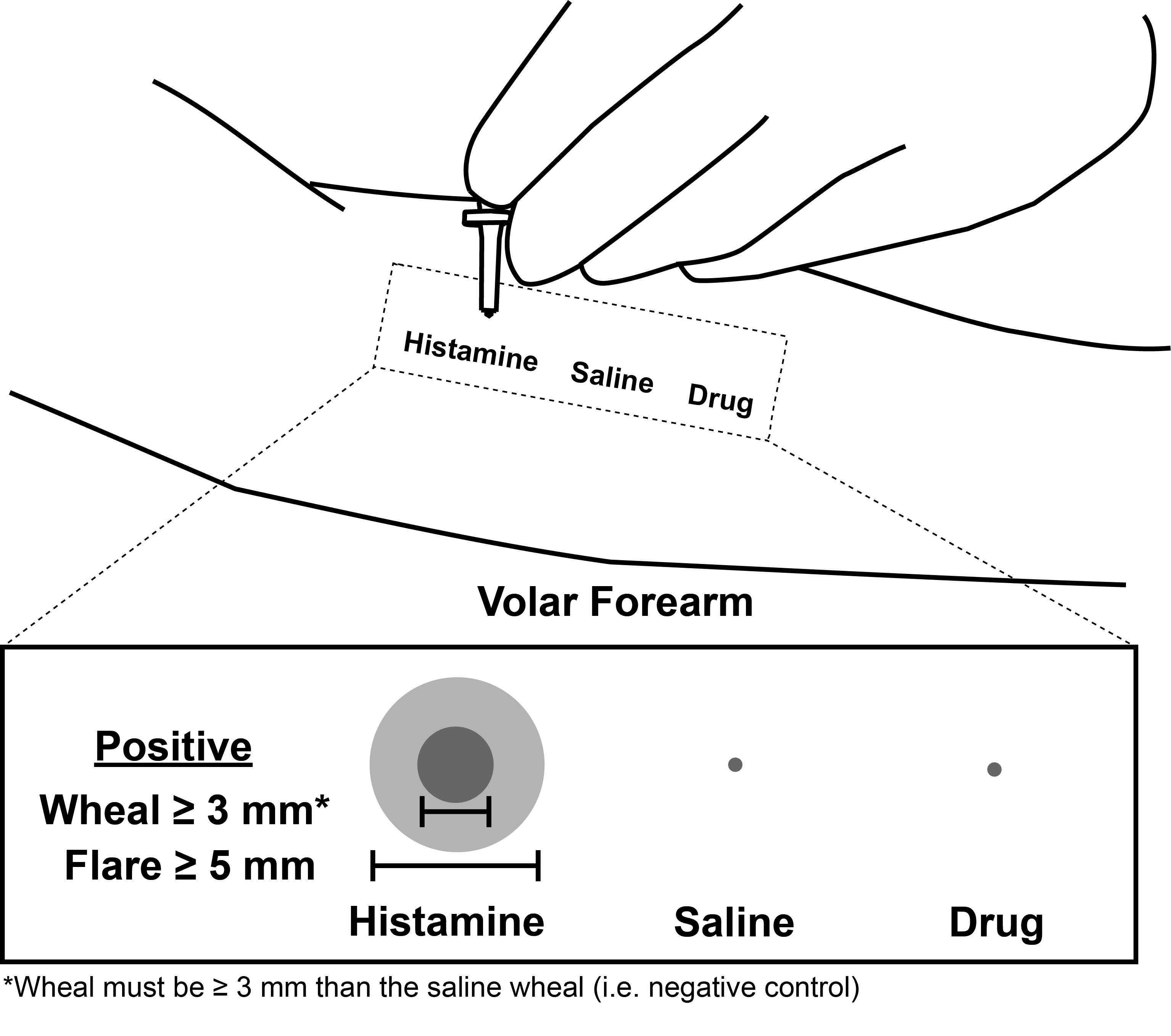
Controls
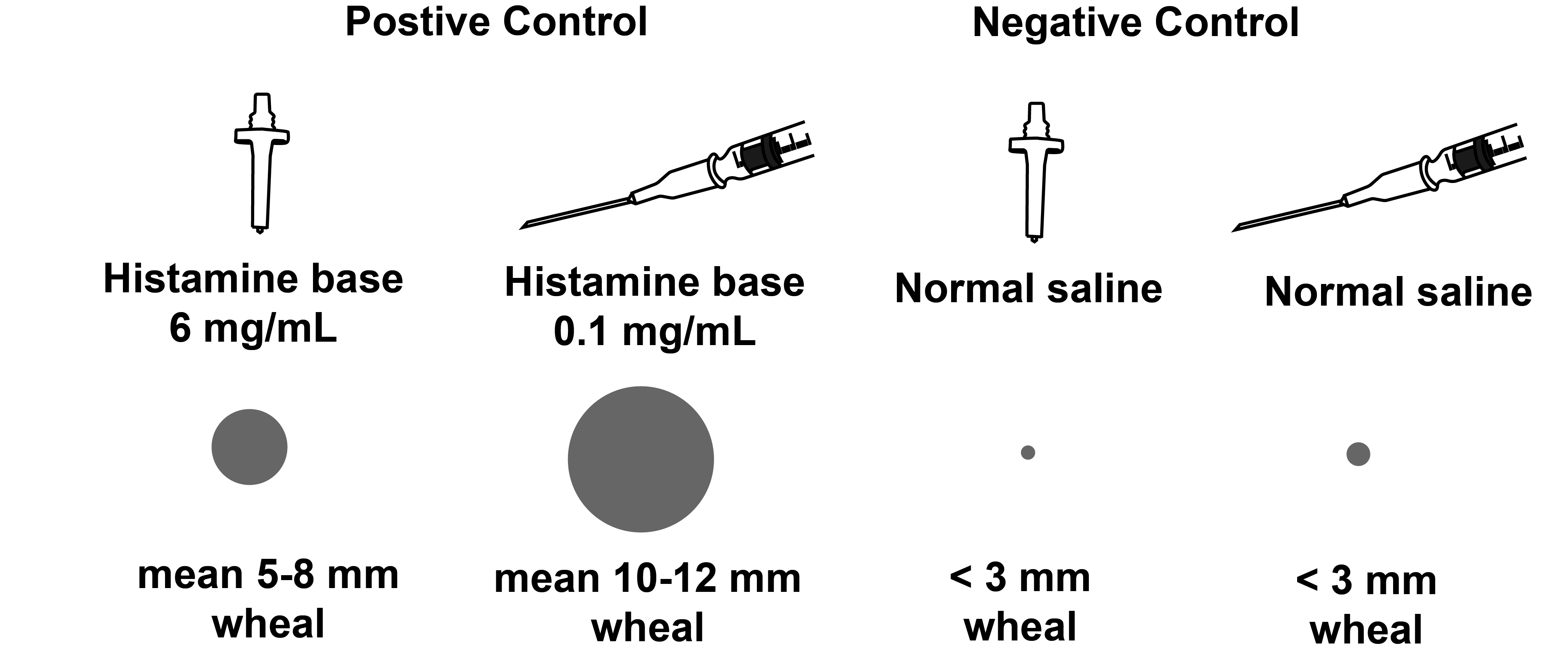 To increase the solubility of histamine in water, it is provided in its salt form, such as histamine dihydrochloride or histamine phosphate. In vivo, histamine dissociates into its biologically active form, called “histamine base.”
To increase the solubility of histamine in water, it is provided in its salt form, such as histamine dihydrochloride or histamine phosphate. In vivo, histamine dissociates into its biologically active form, called “histamine base.”
The histamine and normal saline controls used for skin testing usually also includes 0.4% phenol (also known as carbolic acid) in order to inhibit microbial growth and maintain sterility. Carbolic acid is what Joseph Lister discovered to be an effective antiseptic for surgery.
Increased skin test reactivity - Skin lesion with altered permeability (e.g. atopic dermatitis) - Stress
Decreased skin reactivity - Eczema (but finding is not consistently observed) - Some patients with cancer - Chronic renal failure or on regular hemodialysis - Patients with spinal cord injuries - Peripheral nerve abnormalities (e.g. diabetic neuropathy)
Positive Skin Test
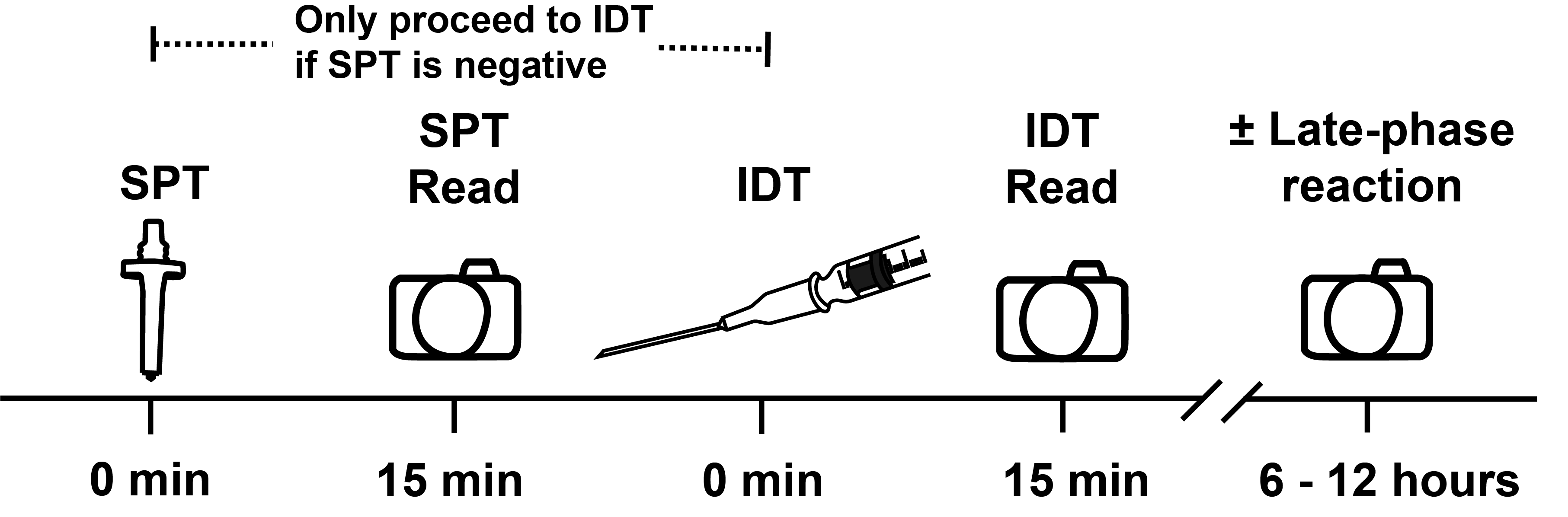
Immediate Reaction
Immediate skin testing starts around 5 minutes and peaks at 15 minutes, resolving around 30 minutes.
Histamine is not the only mediator of the wheal and flare response. Mast cell degranulation also leads to release of the following mediators:
Tryptase
Neurogenic Mediators (e.g. substance P, CGRP, neurokinin A)
Nitric oxide
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
Late phase reaction
Late phase reaction–if occurs–start around 1-2 hours, peak at 6-12 hours, and resolve at 24-48 hours. Not actively/systematically recorded (instruct patients to notify if does occur); however, the exact clinical significance of late phase reactions is unknown.
Concentrations
Oral Challenge
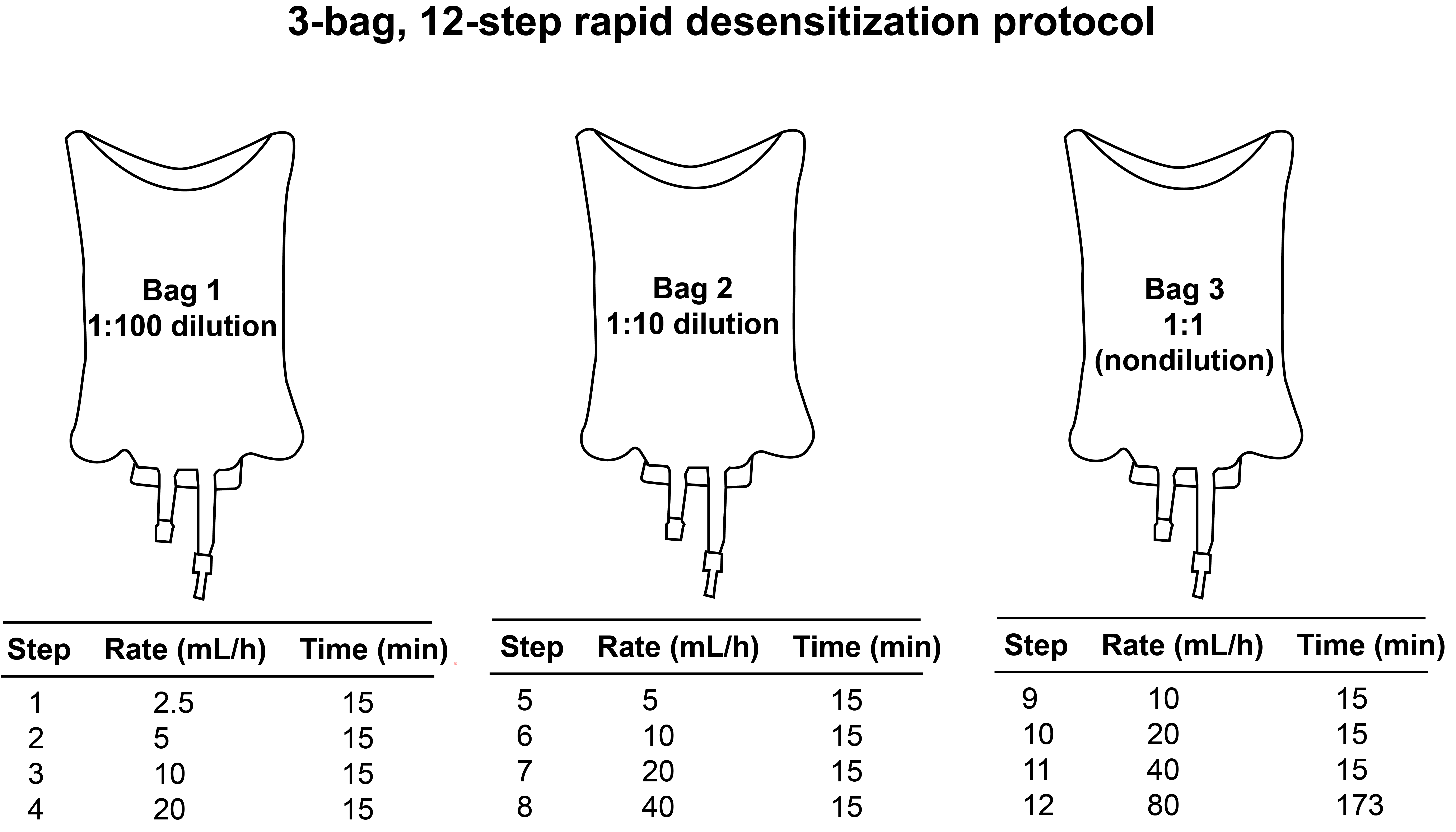
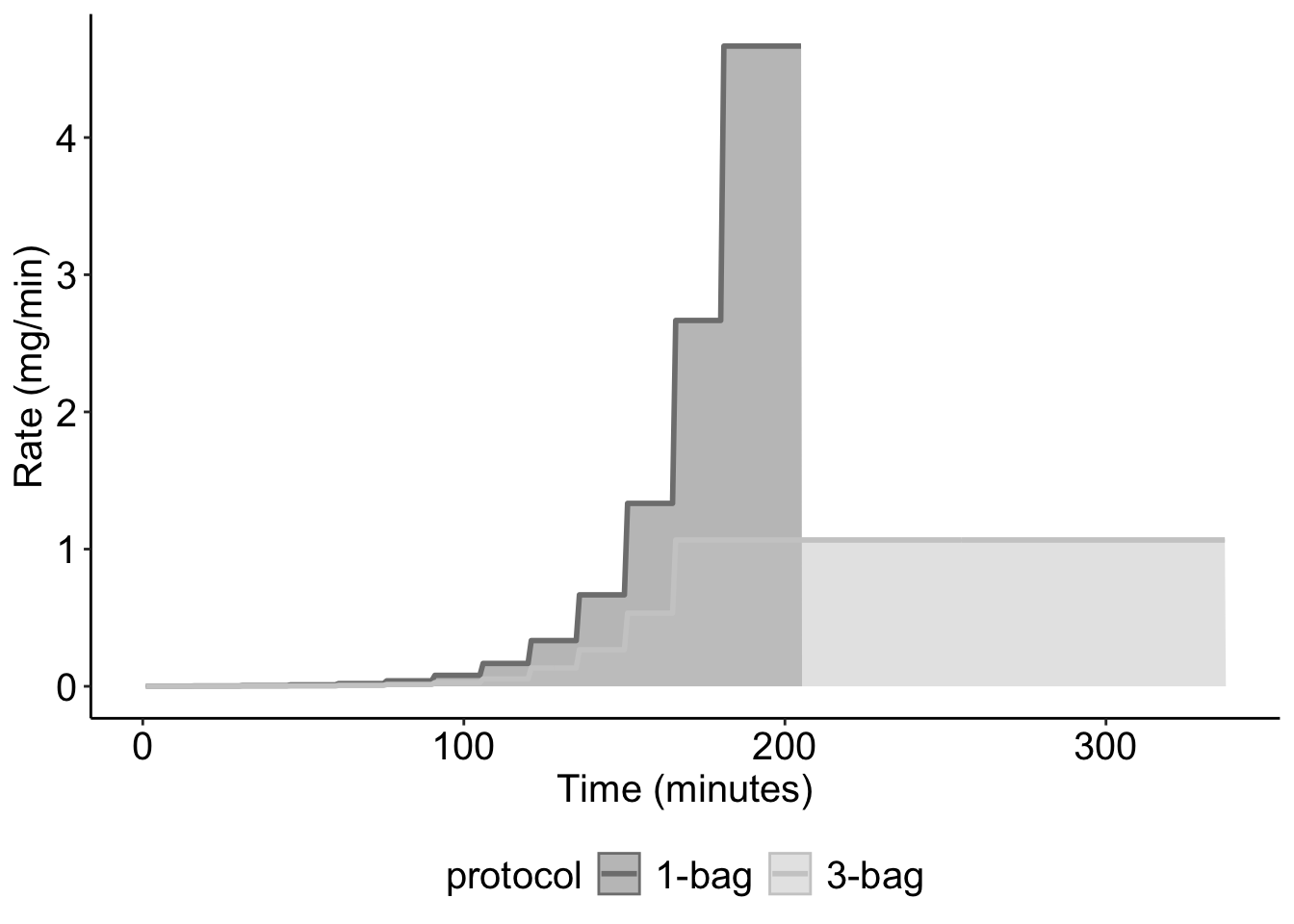
Rapid Desensitization
Figure Generated from protocol comparison from (Lee et al. 2020)
Biomarkers
Tryptase
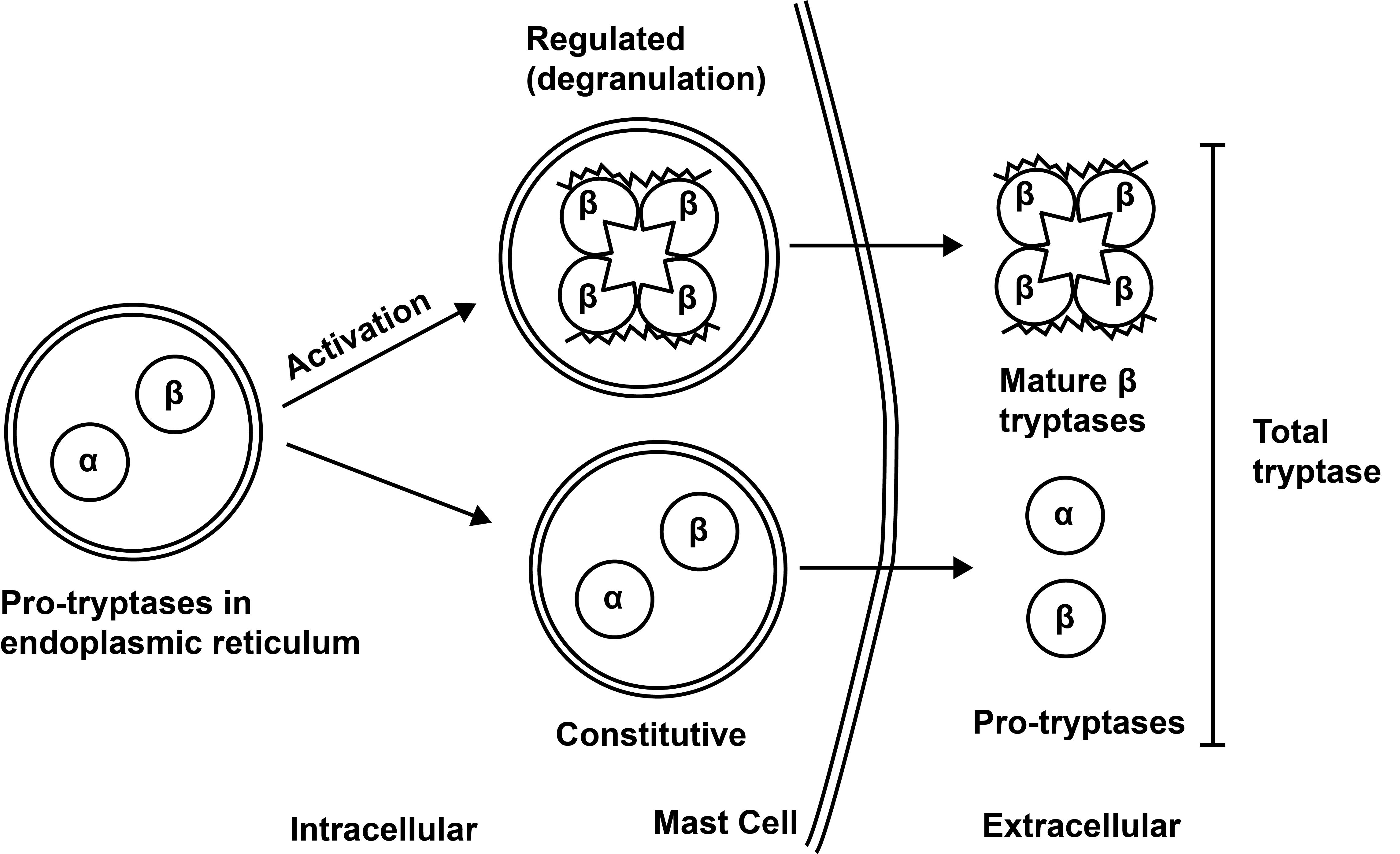
Tryptase is a natural serine protease
average tryptase, average tryptase HAT, average tryptase ISM, average tryptase ASM
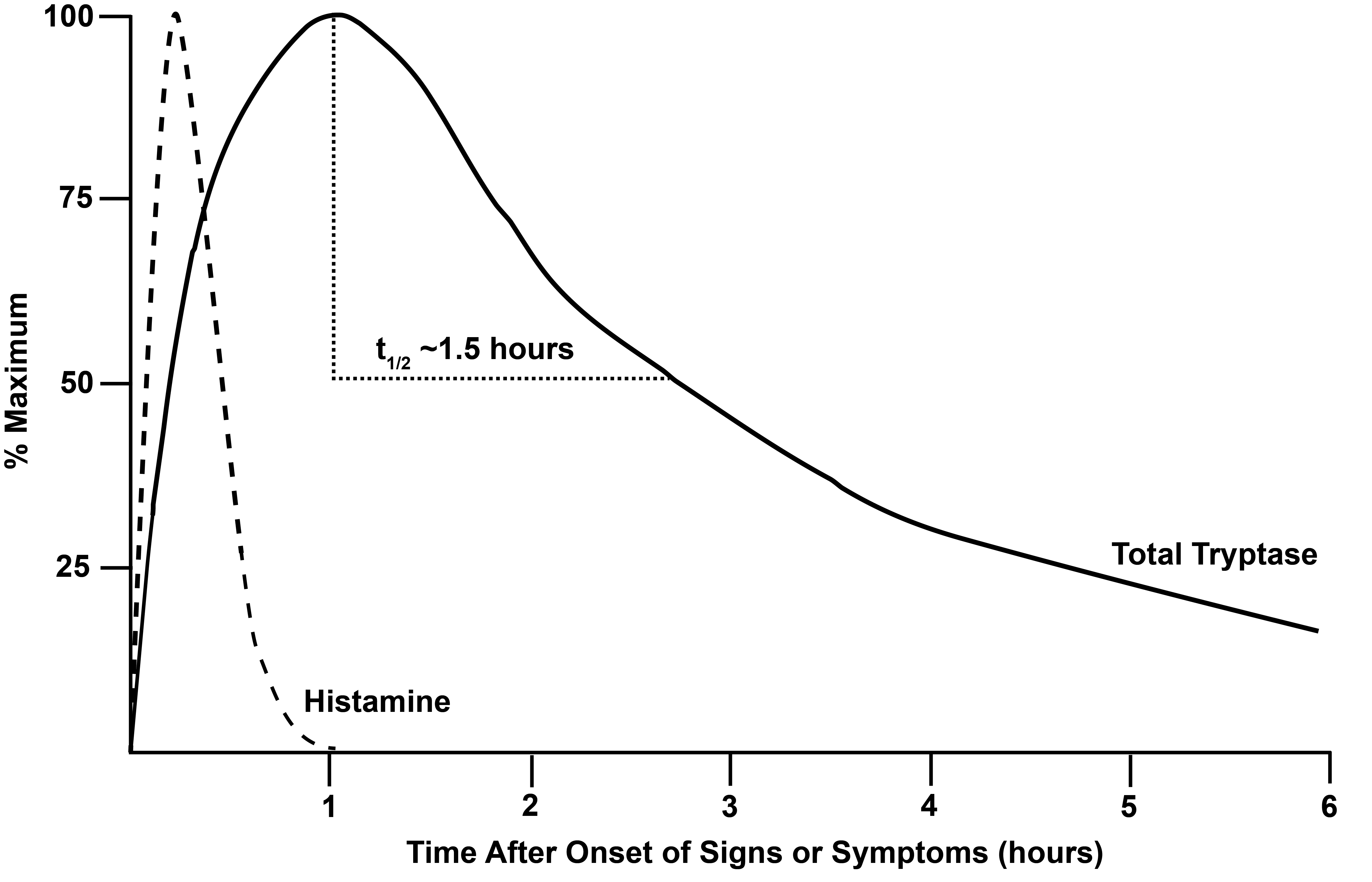
Elevated basal tryptase >= 11.5 ng/mL Can get basal tryptase at 24 hrs after anaphylaxis event
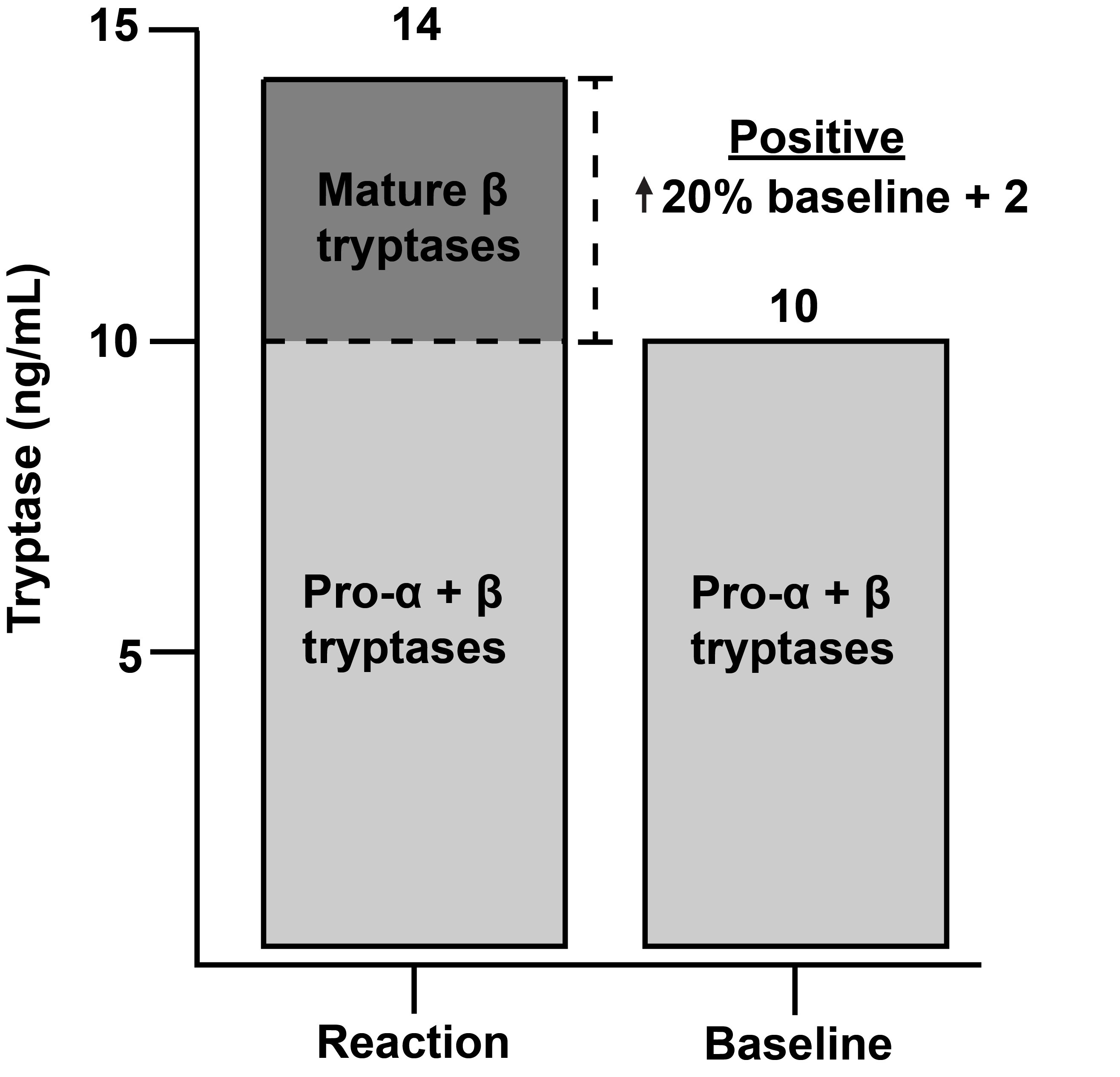
Anaphylaxis >= 20% increase from basal tryptase + 2 ng/mL
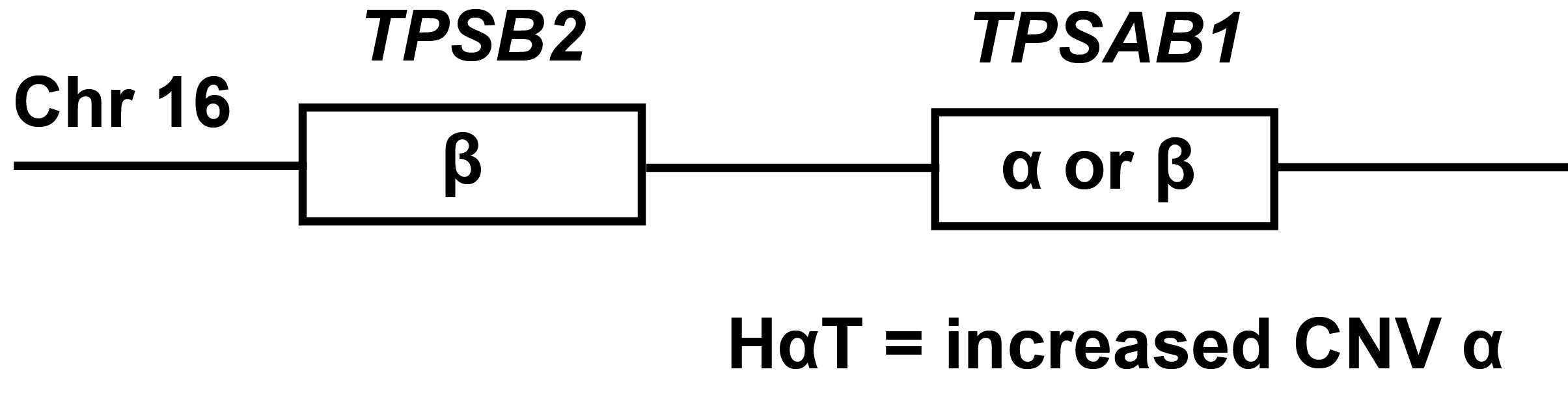
TPSAB1 increased: HaT, SM CNV (alpha tryptase) alpha or beta tryptase constitutively released (measure of MC burden)
TPSB2 Beta preformed granule release during anaphylaxis/severe MC activation
Total Tryptase = a + B by ImmunoCAP (R) In vitro assay half-life ~90 minutes peak at 1 hr stored primarily in MC